Genomic alterations in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (iCCA)
Genomic alterations with potential
therapeutic implications have been
identified in ~40% of iCCA patients,
enabling a more individualised picture
of each patient’s disease biology1
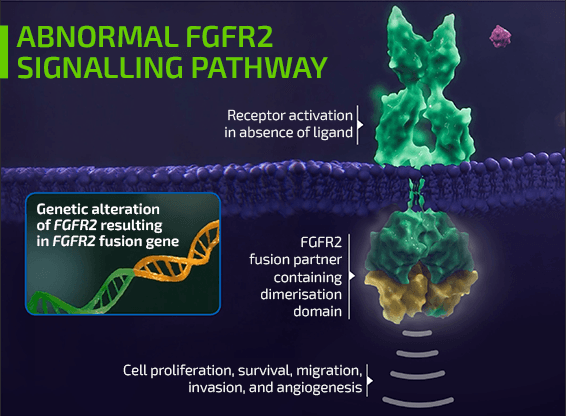
- Two of the most common genomic alterations associated with iCCA include isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (IDH1) mutations and fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (FGFR2) fusions/rearrangements1
Potentially actionable genomic alterations are abundant in iCCA1*

*Based on a retrospective analysis of 6,130 patients diagnosed with iCCA from the FoundationCORE database who received diagnostic panel sequencing on the FoundationOne platform. Short variants, fusions/rearrangements and copy number alterations in >300 tumour-associated genes were evaluated, and the TMB and MSI status were available for the majority of the cohort.1
amp, amplification; BRAF, B-Raf proto-oncogene; BRCA1/2, breast cancer gene 1/2; ERBB2, erb-b2 receptor tyrosine kinase 2; FGFR2, fibroblast growth factor receptor 2; iCCA, intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma; IDH1/2, isocitrate dehydrogenase 1/2; KRAS, Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog; MDM2, mouse double minute 2 homolog 2; MET, mesenchymal epithelial transition proto-oncogene; MSI, microsatellite instability; MSI-H, microsatellite instability-high; mut, mutation; TMB, tumour mutational burden.
Figure adapted from Kendre G, et al. J Hepatol. 2023;78:614–26.1